代码随想录算法训练营第二十三天-39组合总和、40组合总和II、131分割回文串
初步题解
39 组合总和
题目链接:(https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> resultOne = new ArrayList<>();
combinationSumDFS(0, 0, target, candidates, resultOne, result);
return result;
}
private static void combinationSumDFS(int startIndex, int sum, int target, int[] candidates, List<Integer> resultOne, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (sum >= target) {
if (target == sum) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(resultOne));
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
resultOne.add(candidates[i]);
combinationSumDFS(i, sum + candidates[i], target, candidates, resultOne, result);
resultOne.remove(resultOne.size() - 1);
}
}
|
40 组合总和 II
题目链接:(https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> resultOne = new ArrayList<>();
combinationSum2DFS(0, 0, target, candidates, resultOne, result);
return result;
}
private static void combinationSum2DFS(int startIndex, int sum, int target, int[] candidates, List<Integer> resultOne, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (sum == target) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(resultOne));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
if (i - 1 >= startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
resultOne.add(candidates[i]);
combinationSum2DFS(i + 1, sum + candidates[i], target, candidates, resultOne, result);
resultOne.remove(resultOne.size() - 1);
}
}
|
131 分割回文串
题目链接:(https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning)
看解析
39 组合总和
题目链接/文章讲解:(https://programmercarl.com/0039.组合总和.html)
视频讲解:(https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/)
本来以为只要 return 就不用优化了(好像没有什么关系,还是会继续往下走),但是题解中说可以减少一次进入递归。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> resultOne = new ArrayList<>();
combinationSumDFS(0, 0, target, candidates, resultOne, result);
return result;
}
private static void combinationSumDFS(int startIndex, int sum, int target, int[] candidates, List<Integer> resultOne, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (target == sum) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(resultOne));
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {
resultOne.add(candidates[i]);
combinationSumDFS(i, sum + candidates[i], target, candidates, resultOne, result);
resultOne.remove(resultOne.size() - 1);
}
}
|
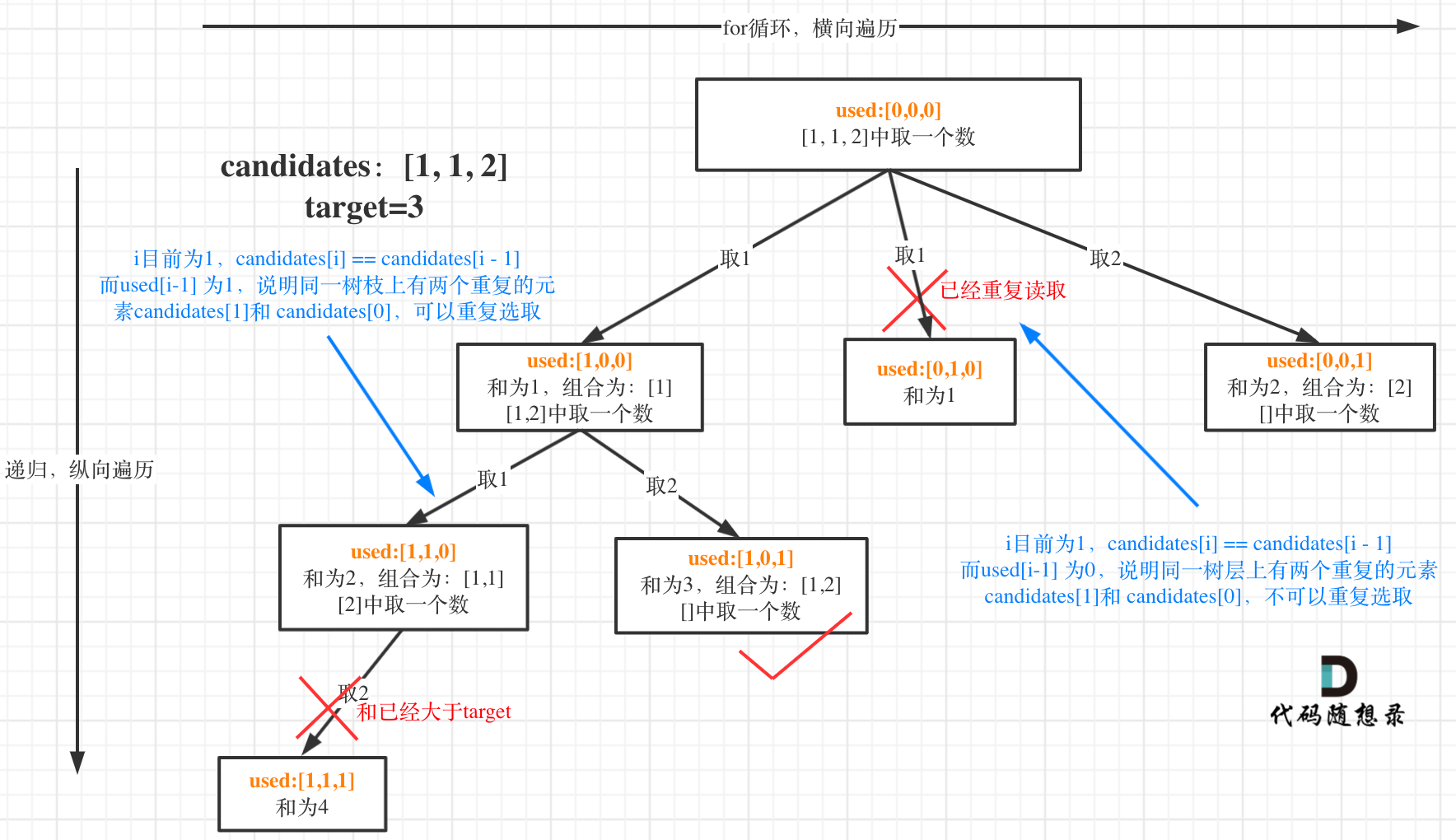
40 组合总和 II
题目链接/文章讲解:(https://programmercarl.com/0040.组合总和II.html)
视频讲解:(https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A/)
![image]()
在 candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] 相同的情况下:
131 分割回文串
题目链接/文章讲解:(https://programmercarl.com/0131.分割回文串.html)
视频讲解:(https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6/)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public static List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> string = new ArrayList<>();
partitionDFS(0, s, string, result);
return result;
}
private static void partitionDFS(int startIndex, String s, List<String> string, List<List<String>> result) {
if (startIndex >= s.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(string));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
String substring = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if (!isPartition(substring)) {
continue;
}
string.add(substring);
partitionDFS(i + 1, s, string, result);
string.remove(string.size() - 1);
}
}
private static boolean isPartition(String substring) {
for (int i = 0, j= substring.length() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (substring.charAt(i) != substring.charAt(j)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
class Solution {
List<List<String>> result;
LinkedList<String> path;
boolean[][] dp;
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
path = new LinkedList<>();
dp = new boolean[str.length + 1][str.length + 1];
isPalindrome(str);
backtracking(s, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(String str, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex >= str.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
} else {
for (int i = startIndex; i < str.length(); ++i) {
if (dp[startIndex][i]) {
path.addLast(str.substring(startIndex, i + 1));
backtracking(str, i + 1);
path.pollLast();
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
}
public void isPalindrome(char[] str) {
for (int i = 0; i <= str.length; ++i) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i < str.length; ++i) {
for (int j = i; j >= 0; --j) {
if (str[j] == str[i]) {
if (i - j <= 1) {
dp[j][i] = true;
} else if (dp[j + 1][i - 1]) {
dp[j][i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
|